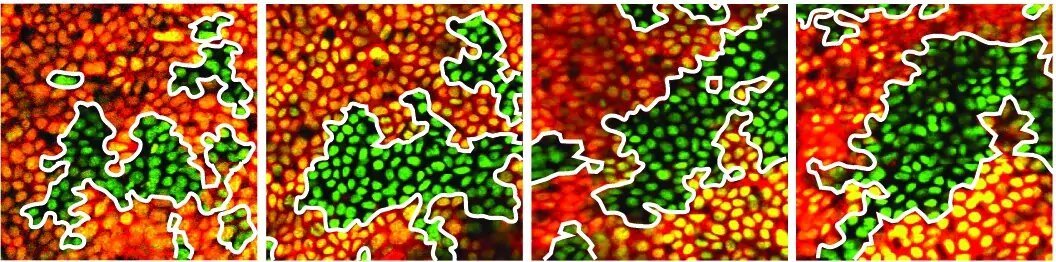
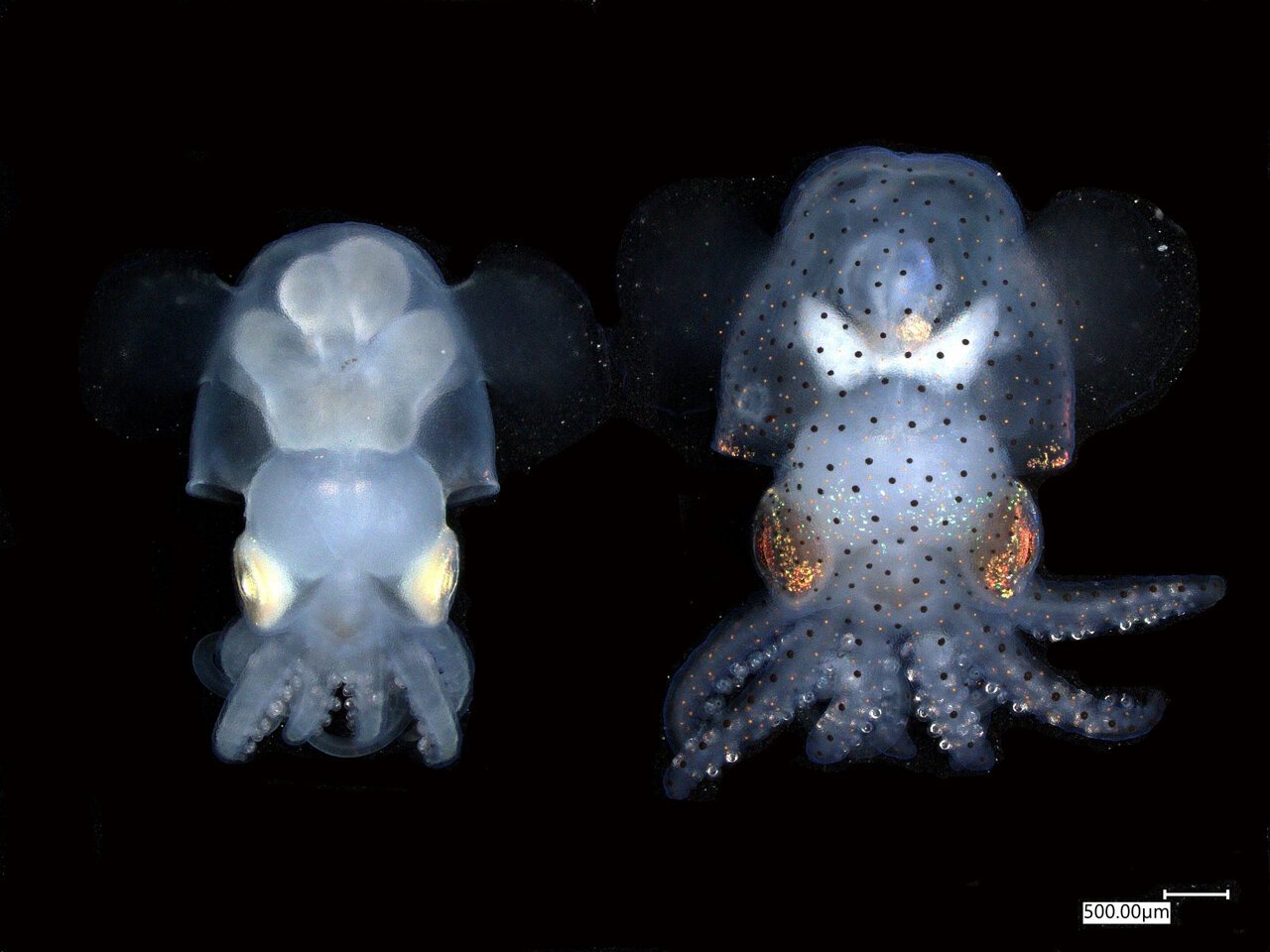
Genome sequencing of antarctic fish reveals how they survive in extreme cold
A team of international researchers, based at esteemed institutions including the University of Cambridge, the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Oslo, as well as institutes in the Netherlands, Switzerland, and the United States, has successfully sequenced the genomes of 24 Antarctic fish species. Their groundbreaking work, which has been published in the prestigious journal … Read more