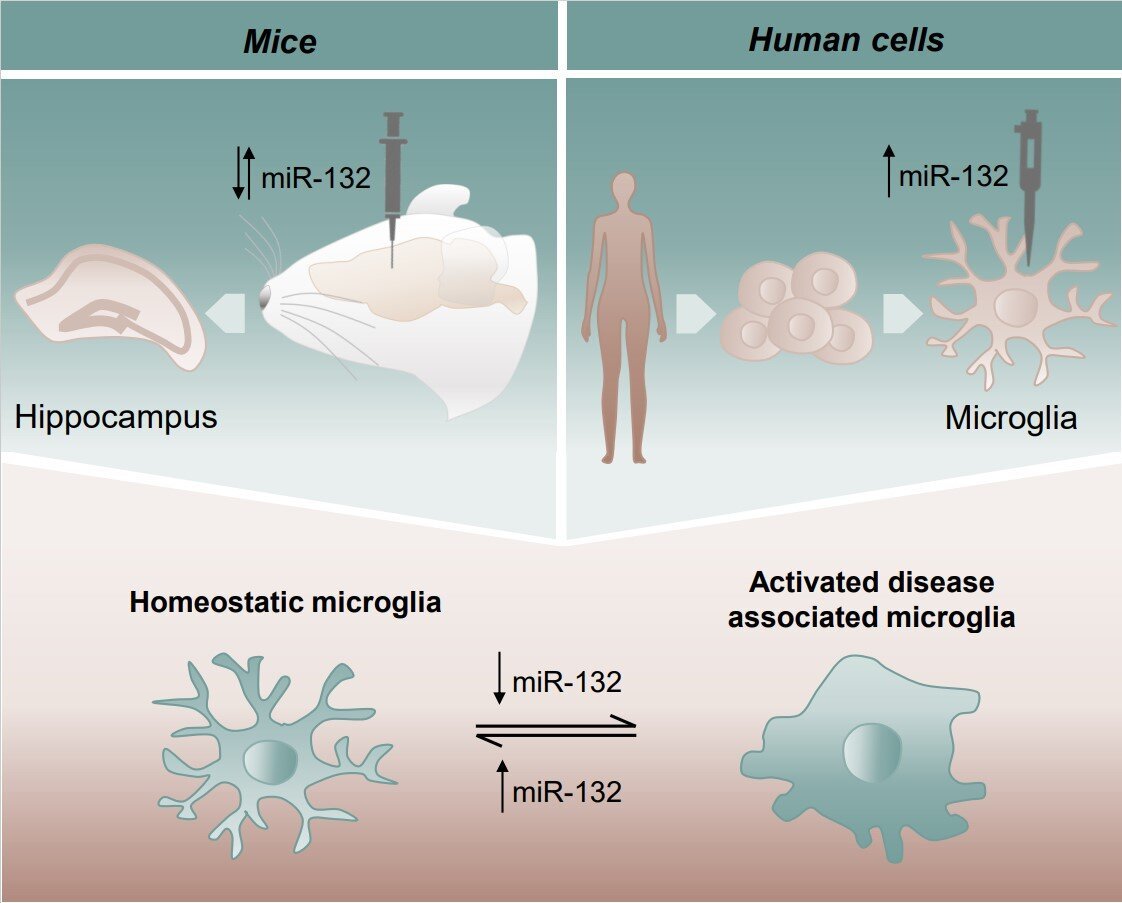
New study finds microRNA-132 may protect against Alzheimer’s disease
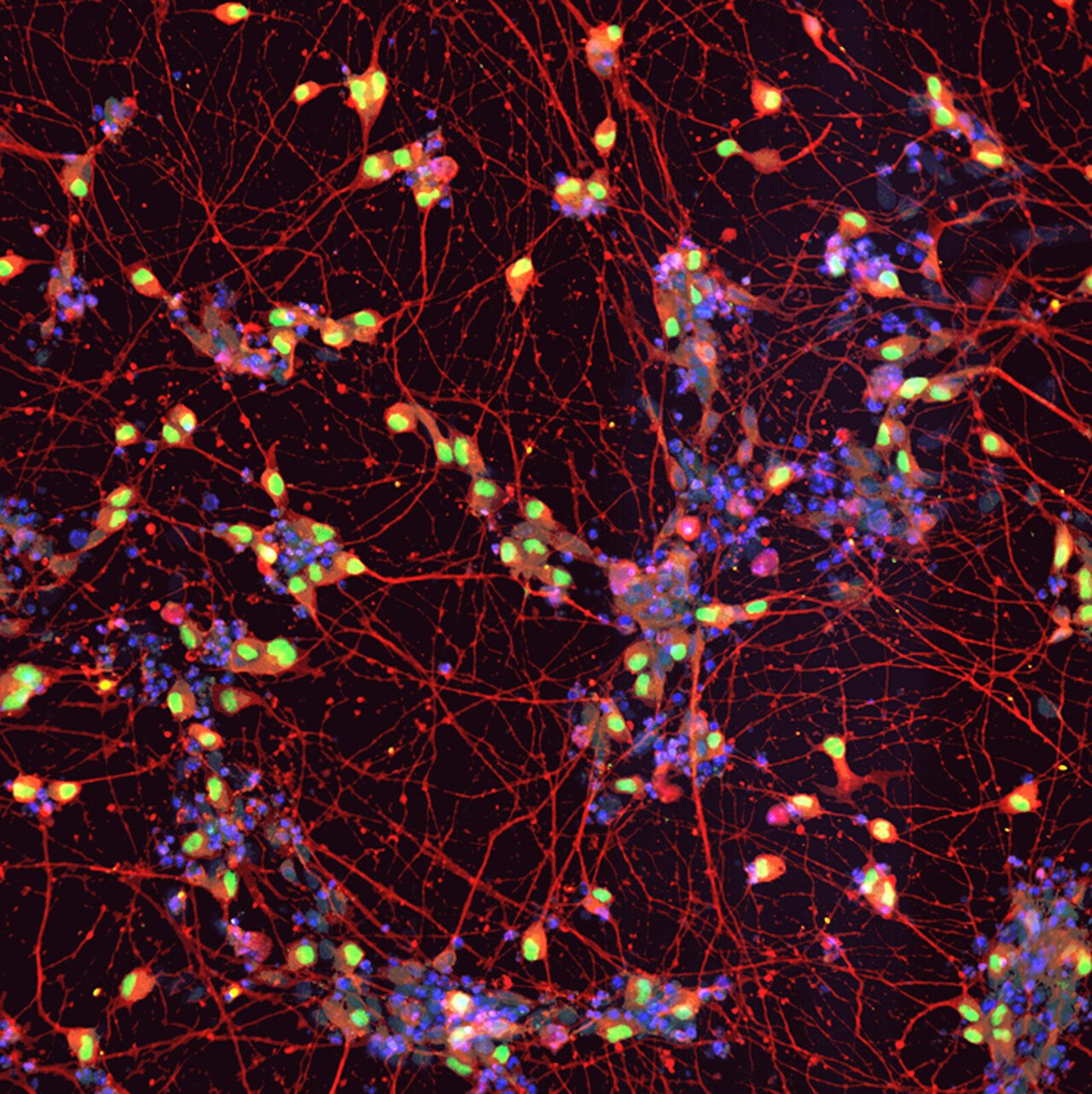
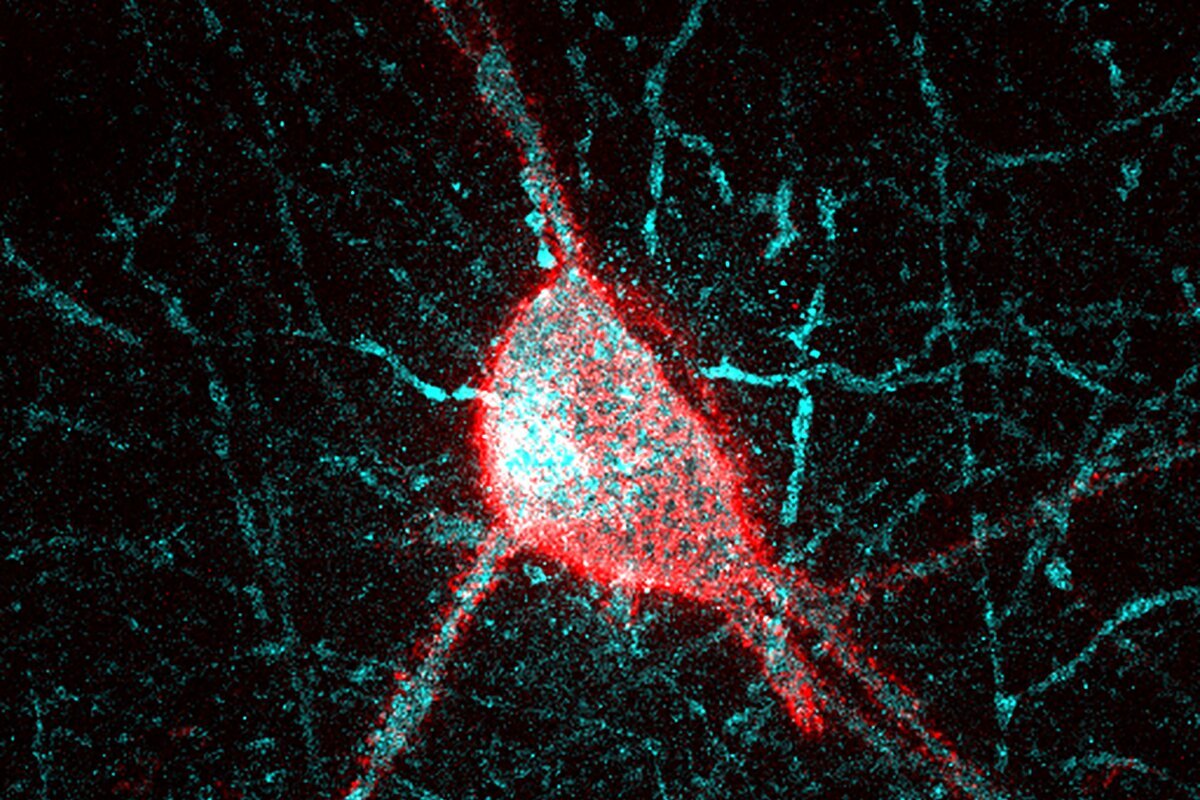
A recent study conducted by the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience and the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain and Disease Research has shed light on the potential impact of a tiny molecule known as microRNA-132 on various brain cells, suggesting its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. RNA, similar to DNA, is composed of interconnected units and has … Read more